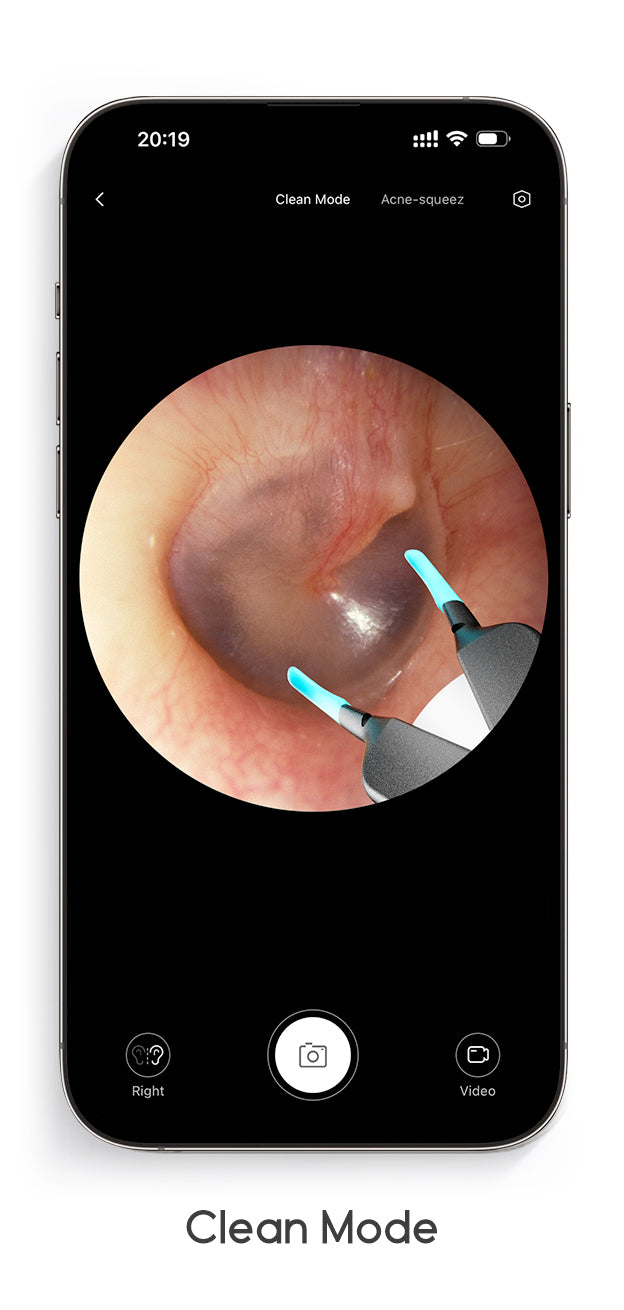
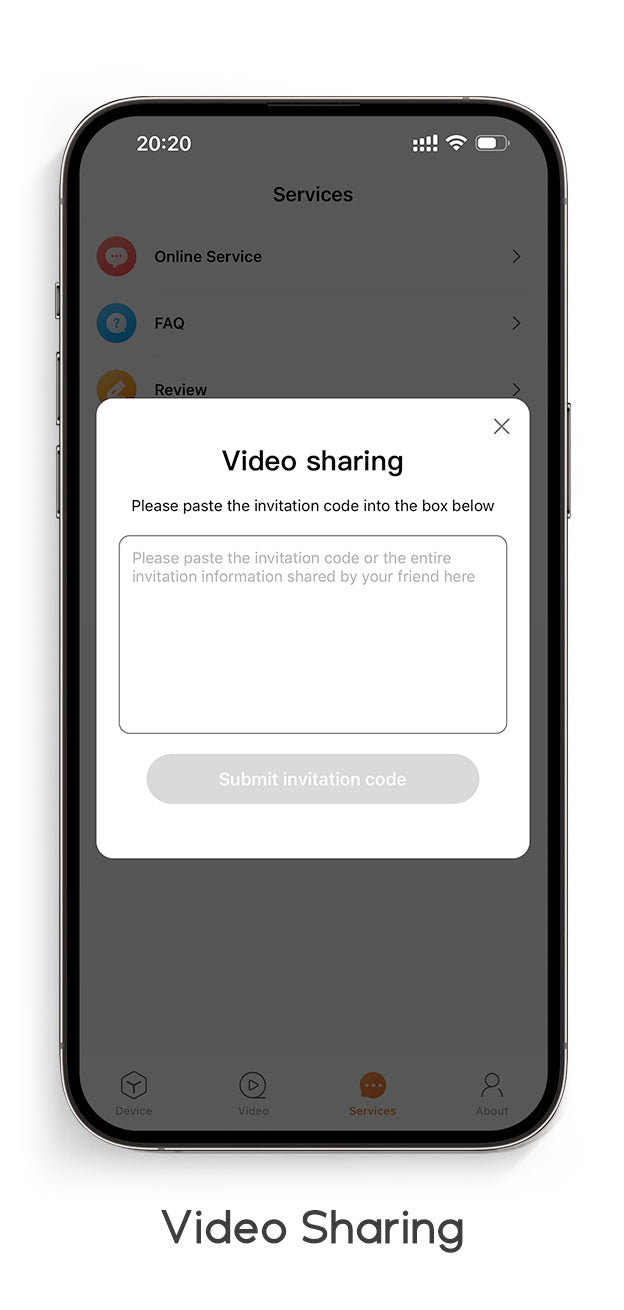
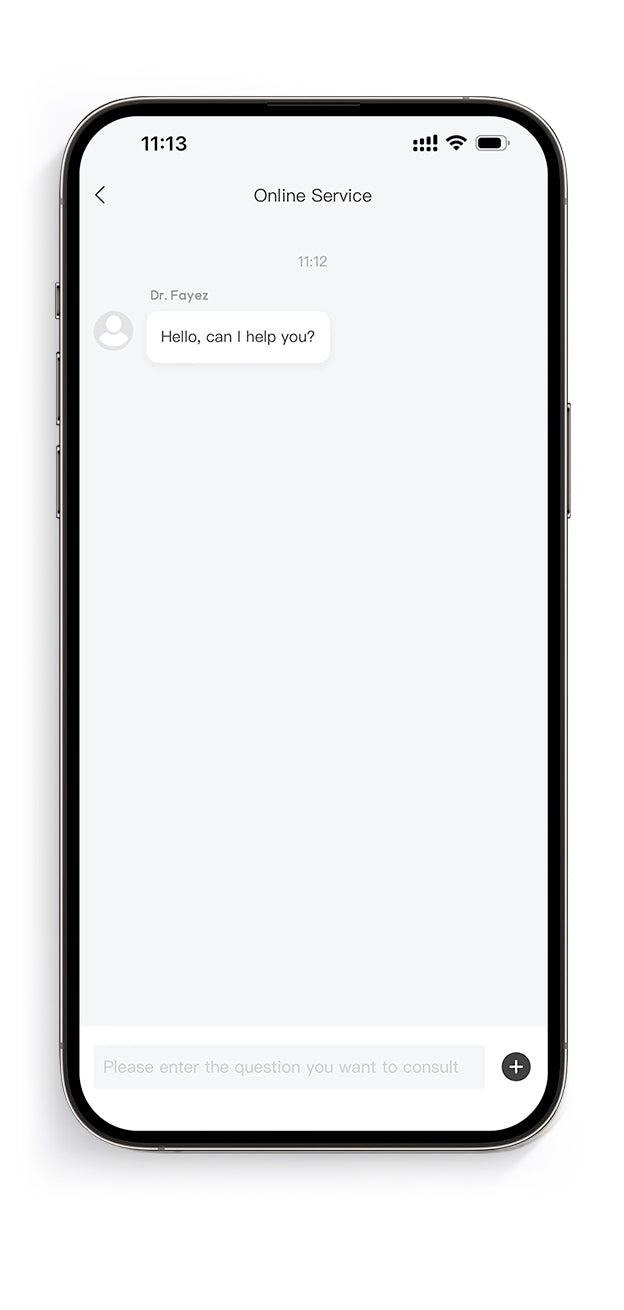
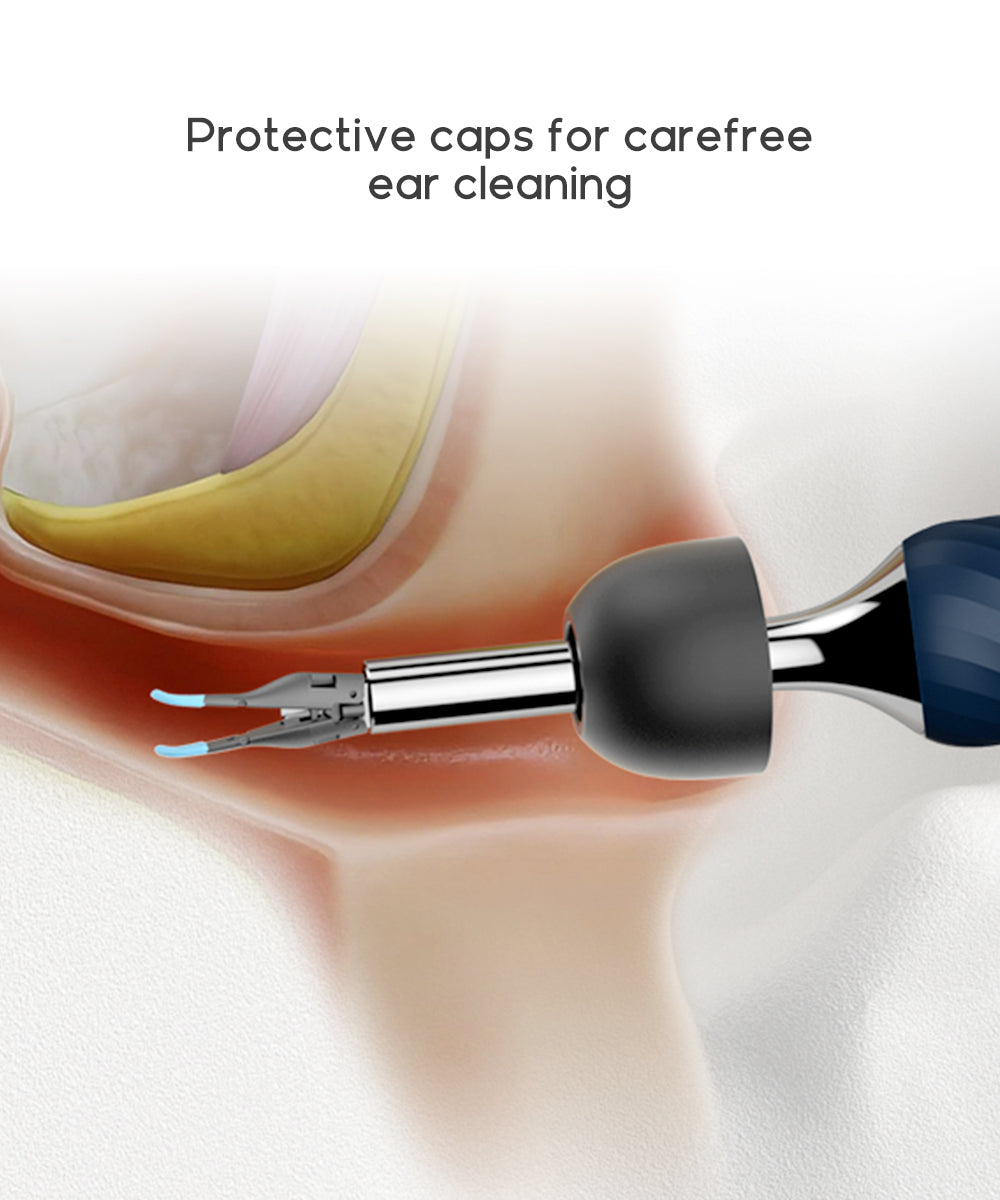
Featured on







Free App - No Subscription Fee Ever
Doctors' testimonials
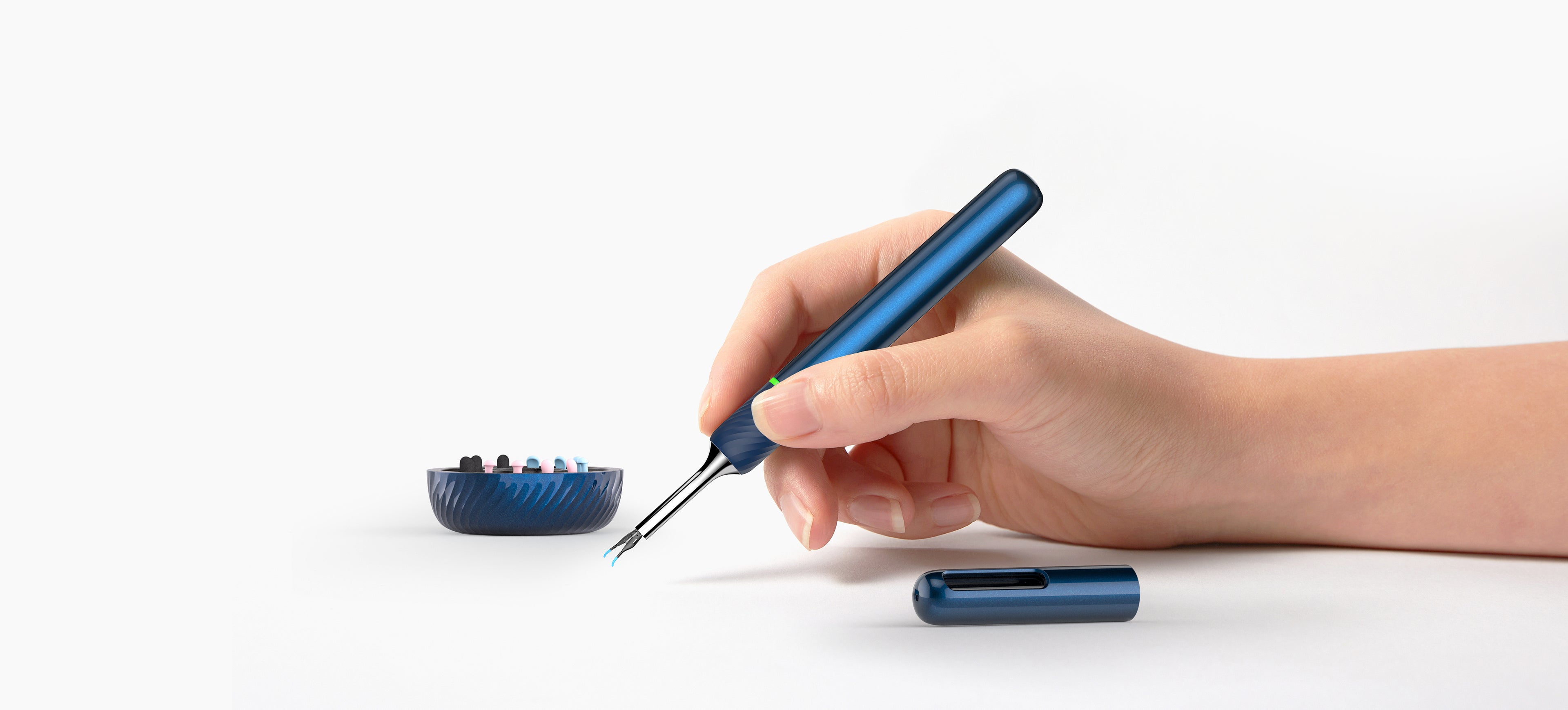
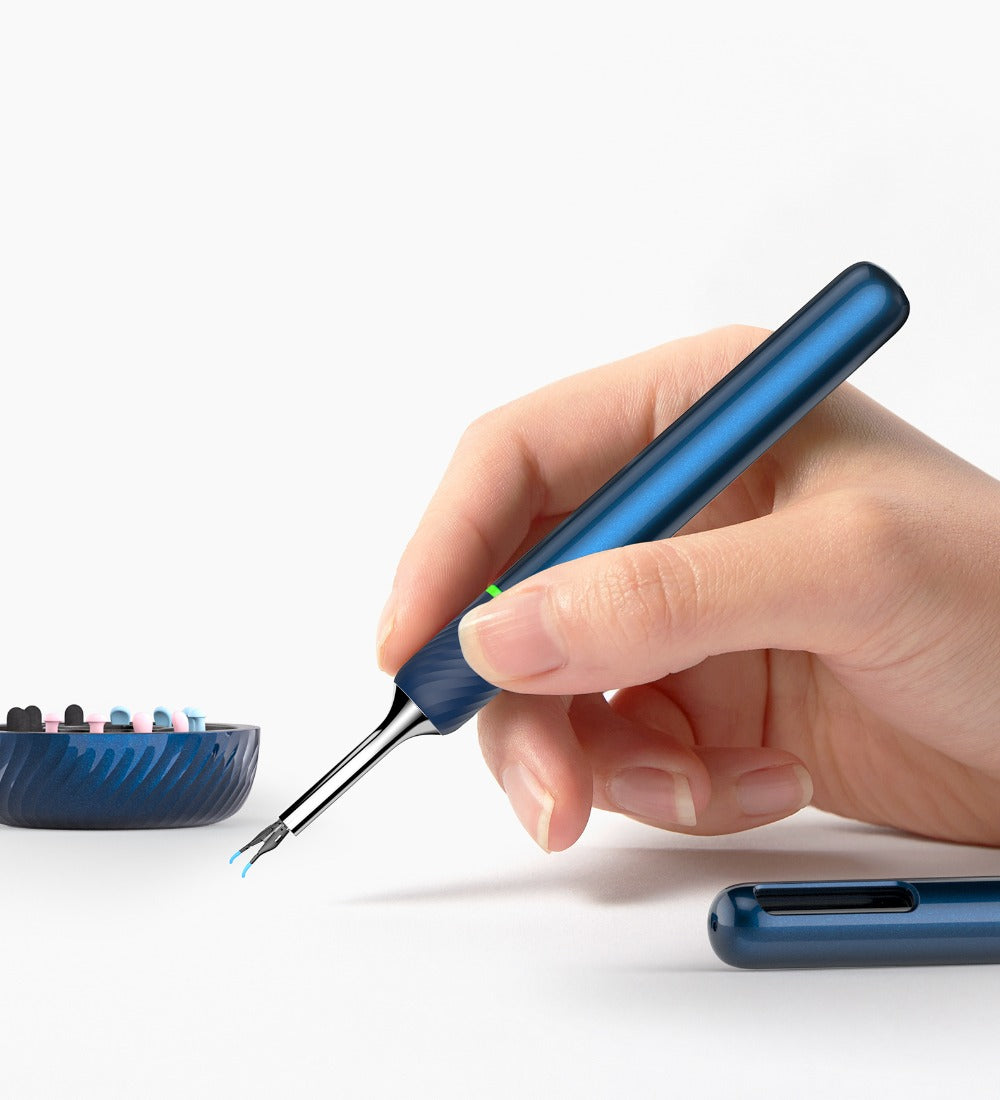
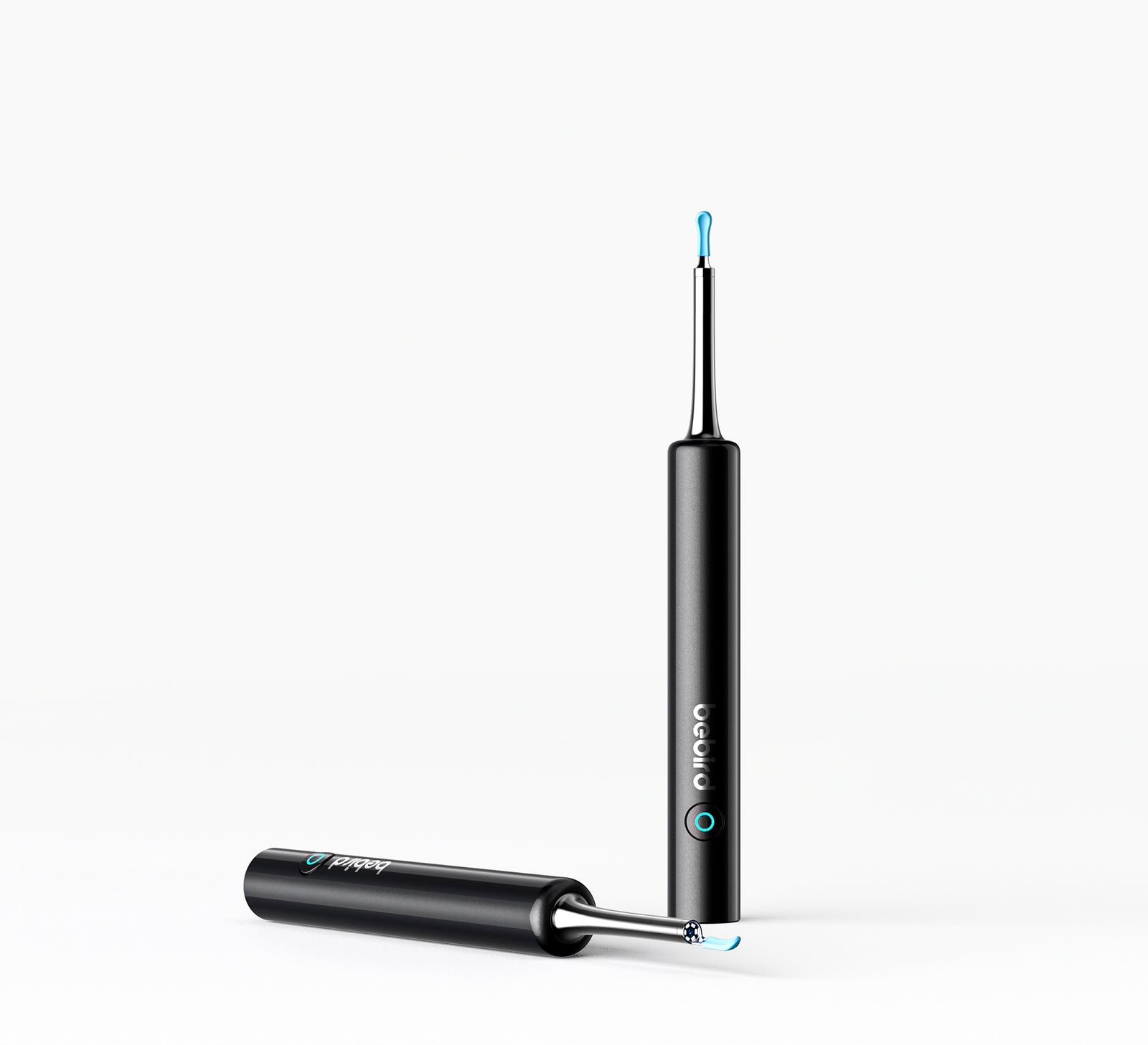
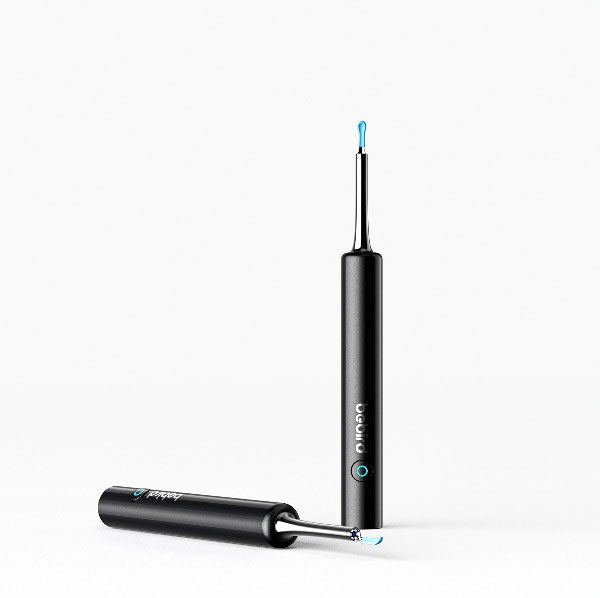
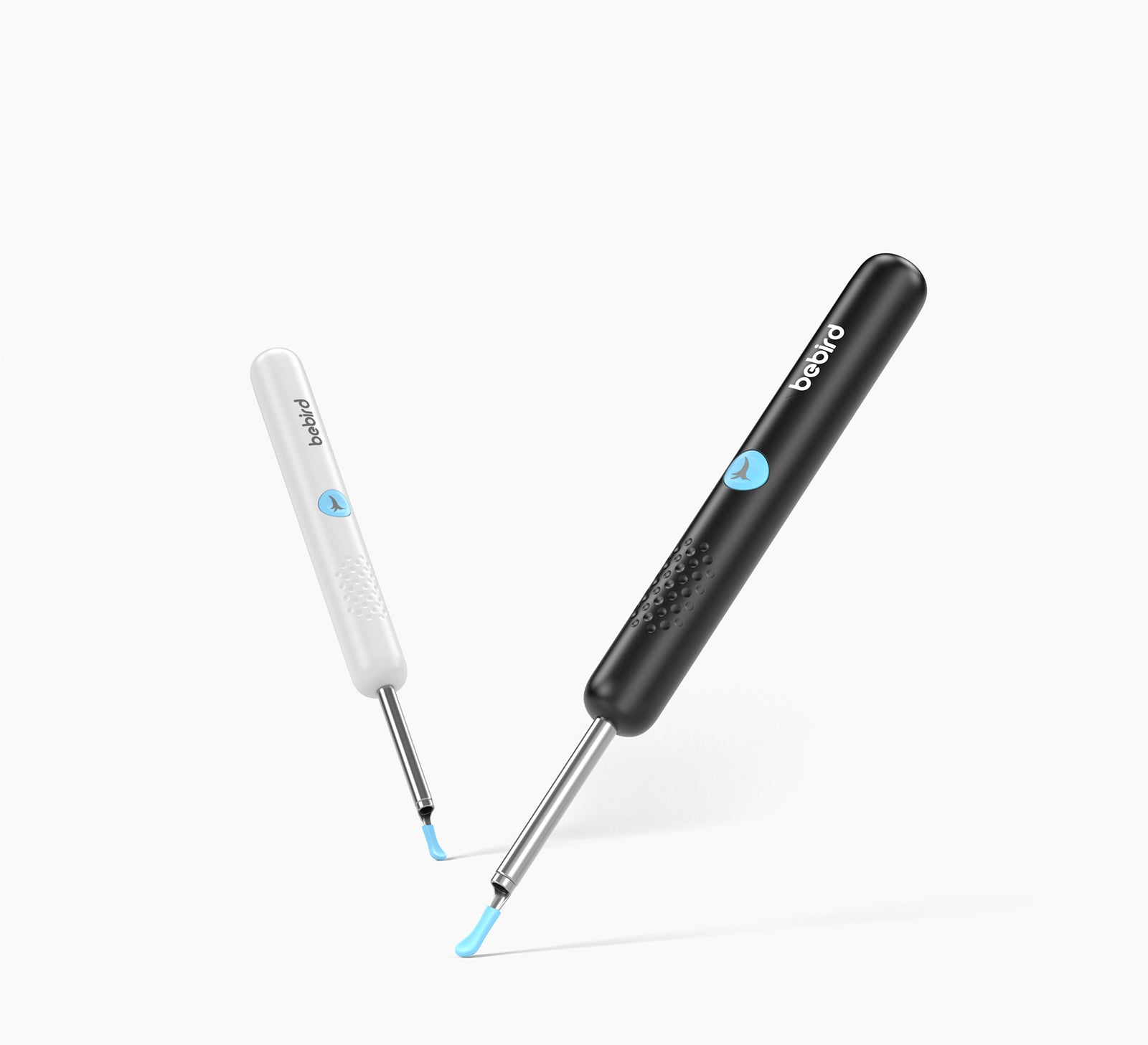
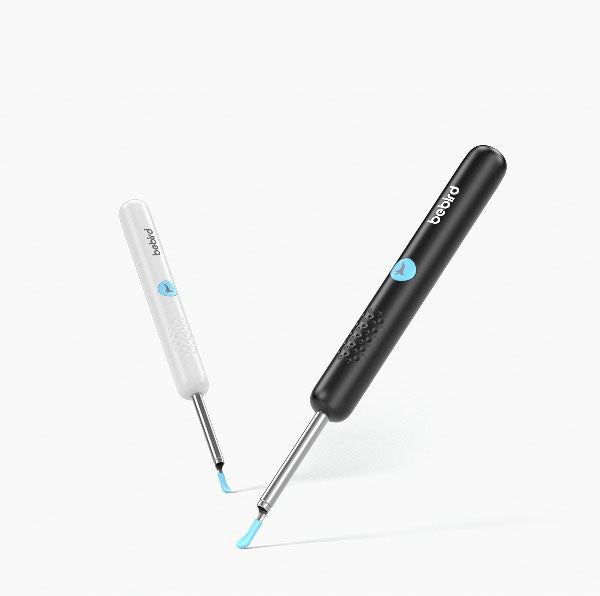
Bebird AuriCare, When Love Resonates In Every Ear Care Moment